
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Short-Term Effects of the Internet-Based Korea Diabetes Prevention Study: 6-Month Results of a Community-Based Randomized Controlled Trial
- Jin-Hee Lee, Sun-Young Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Chan-Jung Han, Ah Reum Jung, Kook-Rye Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):960-965. Published online March 17, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0225
- 5,454 View
- 151 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
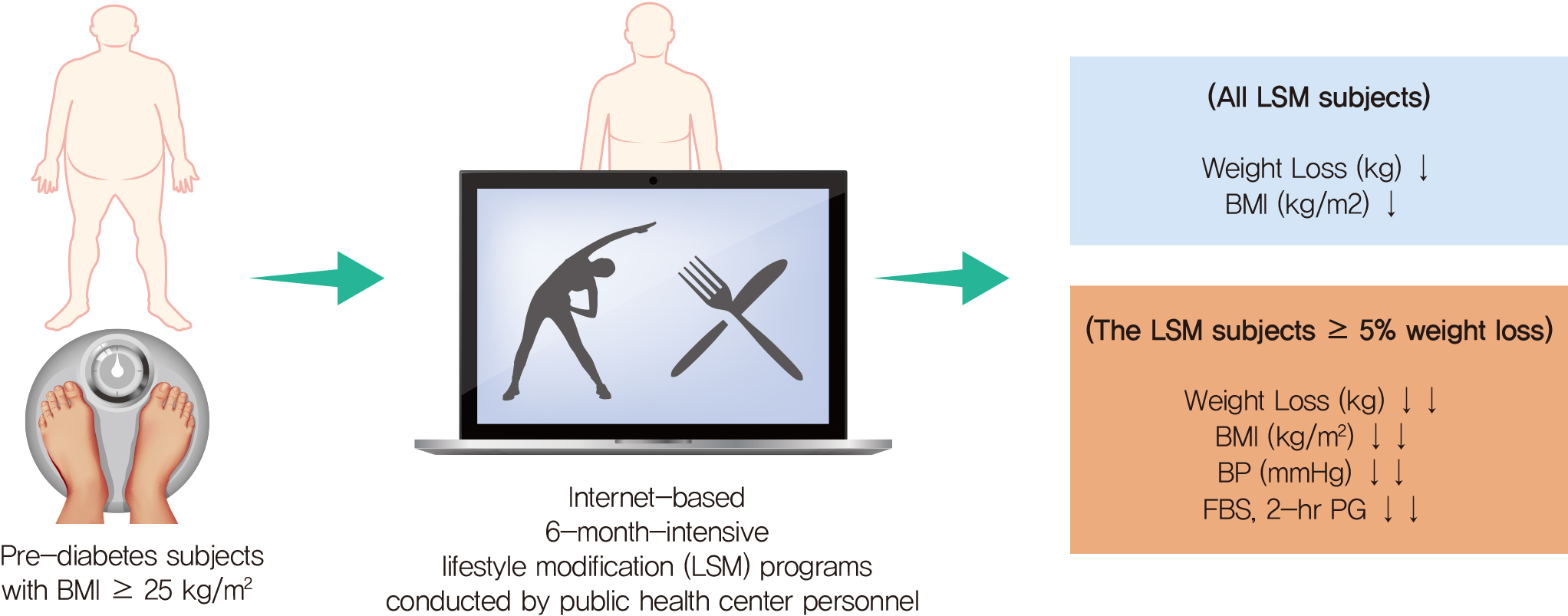
- The aims of this study were to determine the short-term effectiveness of an internet-based lifestyle modification (LSM) program in preventing the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in prediabetes patients in community settings. A total of 415 subjects who were diagnosed with prediabetes were randomly assigned to the LSM and standard management (SM) groups. After the 6-month intervention, the LSM group had a statistically significant reduction in body weight, body mass index compared to the SM group participants. In the LSM group, blood glucose levels were significantly decreased after intervention and the clinical improvement effect was evident in the group that achieved the target weight loss of 5% or more of the initial weight for 6 months. Internet-based 6-month-intensive LSM programs conducted by public health center personnel are an effective way to provide lifestyle intervention programs and encourage maintenance of healthy behaviors in subjects with a high risk of T2DM in community settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- U-shaped association between online information exchange and app usage frequency: a large-scale survey of China ‘s online young and middle-aged people with pre diabetes and diabetes
Hanbin Guo, Yibiao Xiao, Canlin Liao, Jiating Sun, Yanchun Xie, Yitong Zheng, Guanhua Fan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Innovation in diabetes prevention research: The 36-year legacy of China Da Qing diabetes prevention study
Xin Chai, Yachen Wang, Jinping Wang, Qiuhong Gong, Juan Zhang, Ruitai Shao
Chinese Science Bulletin.2023; 68(28-29): 3834. CrossRef - Efficacy of Personalized Diabetes Self-care Using an Electronic Medical Record–Integrated Mobile App in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: 6-Month Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Young Lee, Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Sun-Young Lim, Jin-Hee Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Kun-Ho Yoon, Min Kyung Hyun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2022; 24(7): e37430. CrossRef - Prevention of type 2 diabetes through remotely administered lifestyle programs: A systematic review
Valaree Villegas, Alisha Shah, JoAnn E. Manson, Deirdre K. Tobias
Contemporary Clinical Trials.2022; 119: 106817. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Kyu Yeon Hur, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Jong Ha Baek, Junghyun Noh, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Ye Seul Yang, Jang Won Son, Jong Han Choi, Kee Ho Song, Nam Hoon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jin Wha Kim,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 461. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Seung-Hyun Ko
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 244. CrossRef
- U-shaped association between online information exchange and app usage frequency: a large-scale survey of China ‘s online young and middle-aged people with pre diabetes and diabetes
- Ubiquitous Diabetes Management System via Interactive Communication Based on Information Technologies: Clinical Effects and Perspectives
- Jae-Hyoung Cho, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hoon Han, Jin-Hee Lee, Jeong-Ah Oh, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(5):267-273. Published online October 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.5.267
- 3,619 View
- 28 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader New diabetes management systems based on interactive communication have been introduced recently, accompanying rapid advances in information technology; these systems are referred to as "ubiquitous diabetes management systems." In such ubiquitous systems, patients and medical teams can communicate via Internet or telecommunications, with patients uploading their glucose data and personal information, and medical teams sending optimal feedback. Clinical evidence from both long-term and short-term trials has been reported by some researchers. Such systems appear to be effective not only in reducing the levels of HbA1c but also in stabilizing glucose control. However, most notably, evidence for the cost-effectiveness of such a system should be demonstrated before it can be propagated out to the general population in actual clinical practice. To establish a cost-effective model, various types of clinical decision supporting software designed to reduce the labor time of physicians must first be developed. A number of sensors and devices for monitoring patients' data are expected to be available in the near future; thus, methods for automatic interconnections between devices and web charts were also developed. Further investigations to demonstrate the clinical outcomes of such a system should be conducted, hopefully leading to a new paradigm of diabetes management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a diabetes mobile healthcare system and clinical application in China: a narrative review
Lin Sun, Zhuo Li, Shugang Xi, Huan Wang, Heyuan Wang, Haimin Wang, Ruoxuan Peng, Qin Xu, Mei Gao, Xianchao Xiao, Gang Wang, Yuan Gao, Guixia Wang, Chenglin Sun
Journal of Public Health.2021; 29(6): 1471. CrossRef - A case-control study of pattern and determinants of quality of life of patients with diabetes in a developing country
Ofem Enang, Ogban Omoronyia, Udeme Asibong, Agam Ayuk, Kenneth Nwafor, Annette Legogie
Journal of the Egyptian Public Health Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Effects of Remote Glucose Monitoring and Patient-Centered Education Platform for Patients with Diabetes
Yeoree Yang, Jae-Hyoung Cho
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(4): 204. CrossRef - Low Cost Inkjet Fabrication of Glucose Electrochemical Sensors Based on Copper Oxide
R. Bernasconi, A. Mangogna, L. Magagnin
Journal of The Electrochemical Society.2018; 165(8): B3176. CrossRef - An Internet-based health gateway device for interactive communication and automatic data uploading: Clinical efficacy for type 2 diabetes in a multi-centre trial
Jae Hyoung Cho, Hun-Sung Kim, Seung Hyun Yoo, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Cheol Young Park, Hae Kyung Yang, Joong Yeol Park, Sung Woo Park, Kun Ho Yoon
Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare.2017; 23(6): 595. CrossRef - A systematic review on incentive-driven mobile health technology: As used in diabetes management
Michael de Ridder, Jinman Kim, Yan Jing, Mohamed Khadra, Ralph Nanan
Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare.2017; 23(1): 26. CrossRef - New Directions in Chronic Disease Management
Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(2): 159. CrossRef - Current Clinical Status of Telehealth in Korea: Categories, Scientific Basis, and Obstacles
Hun-Sung Kim, Hyunah Kim, Suehyun Lee, Kye Hwa Lee, Ju Han Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2015; 21(4): 244. CrossRef - Using mobile phones in healthcare management for the elderly
Hun-Sung Kim, Kye-Hwa Lee, Hyunah Kim, Ju Han Kim
Maturitas.2014; 79(4): 381. CrossRef - Future Prospects of Health Management Systems Using Cellular Phones
Hun-Sung Kim, Yunji Hwang, Jae-Ho Lee, Hye Young Oh, Yi-Jun Kim, Hyeon Yoon Kwon, Hyoseung Kang, Hyunah Kim, Rae Woong Park, Ju Han Kim
Telemedicine and e-Health.2014; 20(6): 544. CrossRef - Exploring the Relationship Among User Satisfaction, Compliance, and Clinical Outcomes of Telemedicine Services for Glucose Control
Mi Jung Rho, Si Ra Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seong K. Mun, In Young Choi
Telemedicine and e-Health.2014; 20(8): 712. CrossRef - Therapeutic training: past, present and future
Alexander Sergeevich Ametov, Bulat Iskandarovich Valitov, Natalya Al'bertovna Chernikova
Diabetes mellitus.2012; 15(1): 71. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring: current clinical use
Hun‐Sung Kim, Jeong‐Ah Shin, Jin‐Sun Chang, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Ho‐Young Son, Kun‐Ho Yoon
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2012; 28(s2): 73. CrossRef - Provider and Systems Factors in Diabetes Quality of Care
Kimia Ghaznavi, Shaista Malik
Current Cardiology Reports.2012; 14(1): 97. CrossRef - Effectiveness and safety of a glucose data-filtering system with automatic response software to reduce the physician workload in managing type 2 diabetes
Jae-Hyoung Cho, Yoon-Hee Choi, Hun-Sung Kim, Jin-Hee Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare.2011; 17(5): 257. CrossRef - Effects on diabetes management of a health-care provider mediated, remote coaching system via a PDA-type glucometer and the Internet
Jae-Hyoung Cho, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Hun-Sung Kim, Jeong-Ah Oh, Kun-Ho Yoon
Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare.2011; 17(7): 365. CrossRef
- Development of a diabetes mobile healthcare system and clinical application in China: a narrative review

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





